Understanding Probability Sampling
Category: Data Science
Donghyuk Kim
Introduction
Sampling is a crucial aspect of research and data analysis. In this blog post, we'll explore probability sampling methods, their advantages and disadvantages, and compare different techniques. We'll also delve into the concepts of sampling with and without replacement.
Types of Probability Sampling
Comparison Table of Sampling Methods
| Method | Definition | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Random Sampling (SRS) | Every member has an equal chance of selection | Unbiased, easy to understand | Impractical for large populations |
| Stratified Random Sampling | Population divided into subgroups before sampling | Ensures subgroup representation | Requires knowledge of population characteristics |
| Systematic Sampling | Selects every nth item from the population | Easy to implement | Potential bias if population has patterns |
| Cluster Sampling | Population divided into clusters, then clusters randomly selected | Cost-effective for dispersed populations | Higher sampling error than SRS |
Visual Representation of Sampling Methods
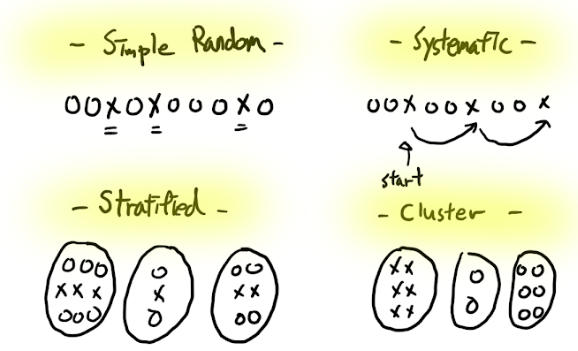
Advantages and Disadvantages of Probability Sampling
Advantages
- Representativeness: Provides a sample that reflects the population.
- Generalizability: Results can be applied to the entire population.
- Statistical inference: Allows for calculation of sampling error.
Disadvantages
- Time-consuming: Can be lengthy to implement, especially for large populations.
- Costly: May require significant resources.
- Complexity: Some methods require advanced statistical knowledge.
Sampling With and Without Replacement
Comparison Table
| Aspect | With Replacement | Without Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Items returned to population after selection | Items not returned after selection |
| Probability | Remains constant for each draw | Changes with each draw |
| Use Case | Modeling certain statistical distributions | More common in practical applications |
| Mathematical Simplicity | Simpler | More complex |
| Realism for Finite Populations | Less realistic | More realistic |
Visual Representation
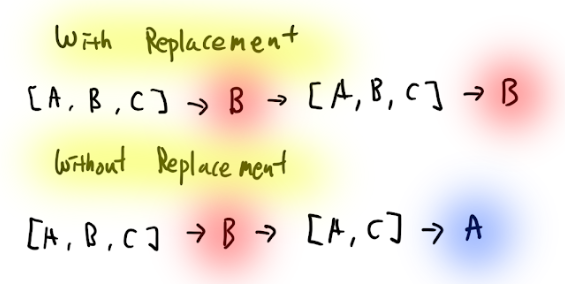
Conclusion
Understanding different probability sampling methods and their characteristics is essential for conducting reliable research. The choice between sampling with or without replacement depends on the specific research context and goals. By carefully considering these factors, researchers can select the most appropriate sampling technique for their studies.
Tags
Sampling SRS Simple Random Sampling Statified Sampling Cluster Sampling Systematic Sampling